Introduction
Healthcare organizations collect and generate tremendous volumes of highly sensitive—and highly regulated—information about patients every day. A substantial portion of this data is personally identifiable information (PII) that qualifies as protected health information (PHI) under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA).
How do organizations keep that information safe? Through effective health information management practices.
Health information management helps organizations improve their handling of health data so they can control access to and maintain data security for that data. Health information managers also perform other vital functions that improve patient outcomes and keep their organizations running smoothly.
In this post, we’ll define health information management and outline its five main functions. We’ll also talk about why health information management is so important and review some of the skills health information management teams need to succeed in 2023. Finally, we’ll explain how proper health information management practices—augmented by technology—can help prevent PII and PHI breaches and protect patients’ sensitive health information.
Contents
Defining personally identifiable information (PII) and protected health information (PHI)
What is health information management?
The importance of health information management
The skills health information management teams need to succeed in 2023
How proper health information management practices can help prevent PII and PHI breaches
How modern technology supports effective health information management
What is PHI & PII?
Before we discuss health information management, we need to lay the groundwork for understanding what personally identifiable information (PII) and protected health information (PHI) are and why they matter.
What does PII stand for in healthcare?
PII is information that has the potential to lead to the identification of an individual, such as a name or identification number.
What does PHI stand for?
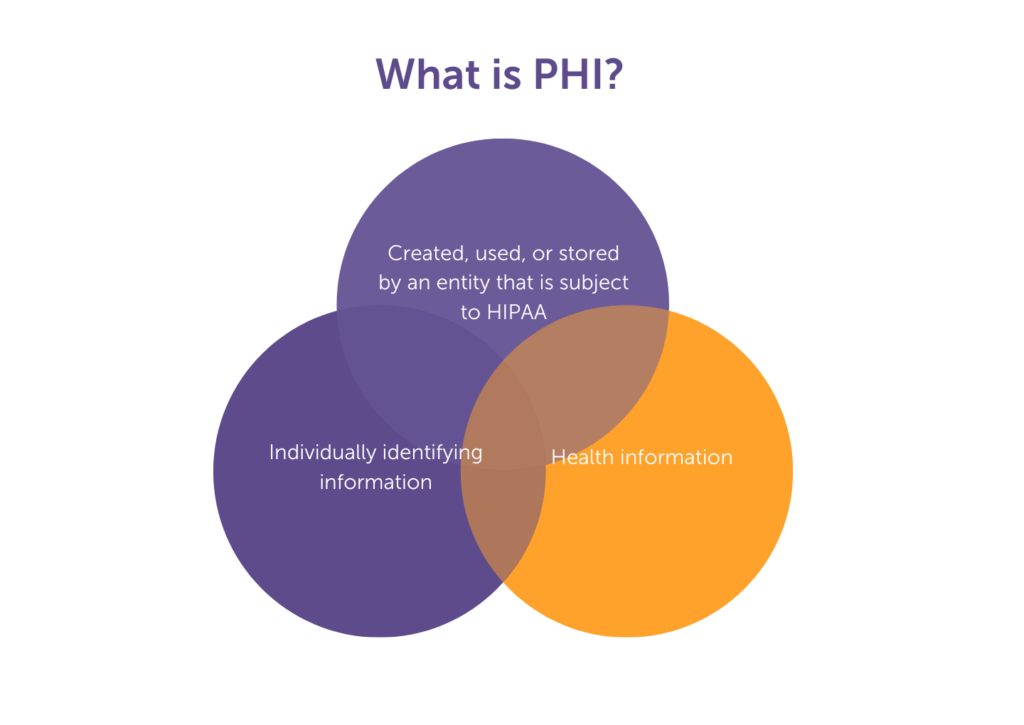
PHI is a subset of PII; it’s a combination of individually identifying information and health information that is created, used, or stored by an entity that is subject to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA).
HIPAA is a federal law that is best known for protecting individuals’ sensitive health information from disclosure without their knowledge or consent. HIPAA does this by requiring healthcare organizations to protect patients’ privacy and safeguard their data from breaches.
Now that we’ve outlined the basics of PII, PHI, and HIPAA, let’s talk about health information management.
What is health information management?
Health information management involves working with healthcare professionals to make sure they properly and securely document and maintain health information. It also encompasses practices that govern how organizations gather, report, analyze, and safeguard health data.
Health information management includes the following five main functions.
1. Coding
Healthcare providers assign billing codes to each diagnosis, service, and procedure their patients receive. The U.S. healthcare industry uses three categories of medical billing codes:
- Current Procedure Terminology (CPT) codes,
- Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) codes, and
- International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes.
Healthcare professionals use these codes to track and bill all kinds of medical and mental health services. Insurance companies use CPT codes in particular to calculate how much they owe providers.
After a healthcare professional has assigned codes for a patient’s treatment, health information managers review those codes and correct any errors to ensure accuracy and consistency throughout the organization.
2. Data analytics
Health data analytics refers to the analysis and interpretation of healthcare data to reveal trends and patterns. Health information managers use data analytics to improve the value of their services and ensure the accuracy, quality, and consistency of their organizations’ data. Data analytics can help healthcare providers maintain data integrity and security, which are critical to improving patient outcomes and complying with laws and regulations that govern how health information is handled.
3. Informatics
Healthcare informatics is “the integration of healthcare sciences, computer science, information science, and cognitive science to assist in the management of healthcare information.” Healthcare informatics uses innovative technology to collect data that is then used to promote the effective management of health information and streamline information workflows. Health information managers use healthcare informatics to map data and oversee and improve their organizations’ processes.
4. Revenue flow
Health information management also involves tracking revenue flow through each stage of a healthcare organization’s revenue cycle. A healthcare provider’s revenue cycle begins when the patient gives their preliminary information to the provider and ends when the patient or their insurance company pays the bill in full.
The revenue cycle includes six stages:
(1) the patient registers with the provider;
(2) the provider renders services;
(3) the provider assigns billing codes to the services and determines how much the services cost;
(4) the provider generates and submits a claim to the patient’s insurance company;
(5) the provider collects payments from the insurance company; and
(6) the provider calculates the patient’s balance, if any, and collects payment on any outstanding amounts.
5. Information governance
Information governance is a set of rules and policies that organizations use to decide who handles data and how. These rules and policies can help organizations avoid data-related issues, lawsuits, and regulatory actions.
Information governance is especially important for healthcare providers because they deal with such high volumes of PII, PHI, and other sensitive data. Therefore, health information managers must ensure that their organization has updated, easy-to-understand information governance policies and enforcement mechanisms in place.
Let’s turn now to the overall importance of effective health information management.
The importance of health information management
Health information management (HIM) is an important part of operating a healthcare organization for three reasons.
First, health information management ensures the accuracy and security of the health information that an organization maintains. Managing a patient’s information so that it is correct, up to date, and available when needed is essential for positive patient outcomes.
Second, health information management enables organizational efficiency by streamlining workflows, clarifying technology needs, and identifying unnecessary expenses so that organizations can refine their budgets.
Third, health information management aids in legal and regulatory compliance by ensuring the application of appropriate information governance principles and protecting PII, PHI, and other sensitive data from unauthorized disclosure.
To bring these benefits to fruition, health information managers must possess certain skills, which we’ll explore below.
The skills health information management teams need to succeed in 2023
Health information management operates at the intersection of healthcare, business, and technology. This means that health information managers need to have a working knowledge of each of these disciplines to succeed.
First and foremost, health information managers must have an understanding of health science, including anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology, so that they can understand the health data they manage.
On the business side, health information managers need basic knowledge about finances and budgets. They also require soft skills such as creative problem-solving, excellent attention to detail, solid communication skills, and emotional intelligence.
As for technology, health information managers must be comfortable with modern technology and have the capacity to learn how to use and implement new software.
Through proper application of these skills, health information managers can improve their organizations’ data management practices and help prevent PII and PHI breaches. Here’s how.
How proper health information management practices can help prevent PII and PHI breaches
Proper health information management practices can help prevent PII and PHI breaches. Best practices for managing health information include:
- taking inventory of the organization’s data regularly,
- detecting and correcting potential risks promptly,
- culling unnecessary and outdated data routinely,
- limiting access to data to those users who require it to do their jobs,
- requiring that users pass through multiple checkpoints before gaining access to data,
- training staff to detect cyber threats and report them immediately,
- making a plan for responding to security and data breaches, and
- investing in technology.
Let’s take a closer look at that last point: how can modern technology support HIM efforts to prevent PII and PHI breaches?
How modern technology supports effective health information management
IPRO specializes in designing tools that can help healthcare organizations manage their data efficiently so that they can avoid the risks associated with data breaches or unauthorized data access.
IPRO technology can help health information managers add value to their organizations by:
- connecting to data in real time so you can search, review, and analyze that data in place;
- leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) technology to more rapidly gain insights;
- identifying weaknesses so you can take corrective actions to prevent data breaches;
- archiving health information in compliance with HIPAA and other document retention laws and regulations;
- protecting PII, PHI, and other sensitive information from unauthorized access and retrieval; and
- reducing the overall amount of sensitive data you must manage by culling duplicate, unnecessary, and outdated data.
For example, Live Early Data Assessment (Live EDA) can rapidly provide valuable insights into your organization’s data and your current management practices. Live EDA allows you to handle large volumes of data quickly and efficiently, automatically identify PII, PHI, and other sensitive information, and send sensitive information to the appropriate reviewers without compromising data security.
To learn more about IPRO and Live EDA, contact us or schedule a meeting with one of our experts today.



